Benjamin Graham’s journey is often described as the foundation story of value investing. Here’s a complete overview of his life and impact:
Early Life (1894–1914)
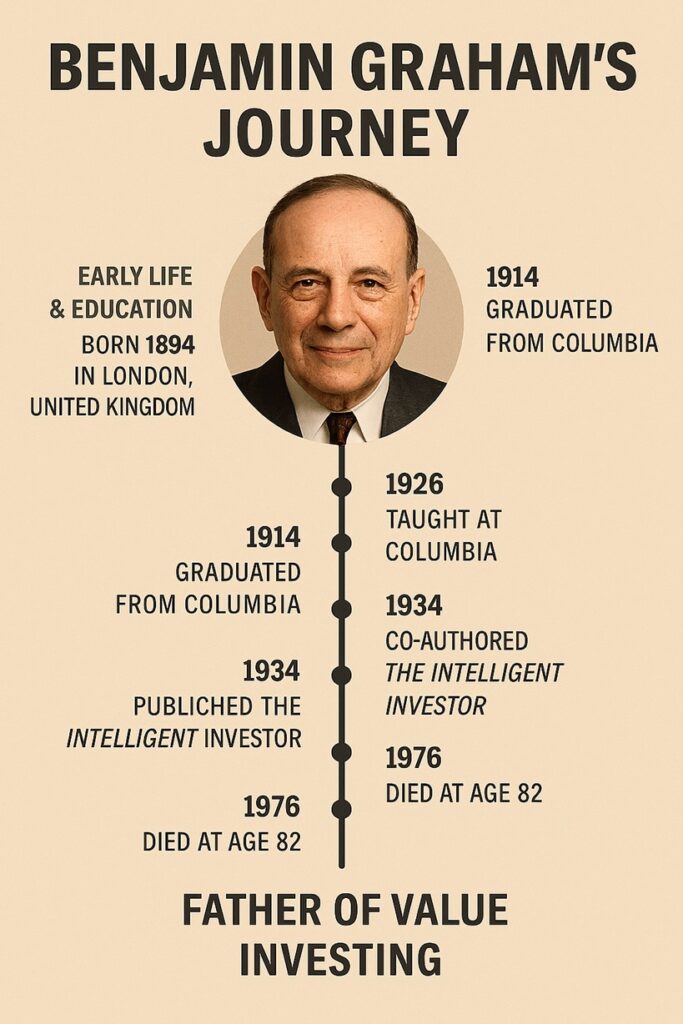
- Born: May 9, 1894, in London, England. His birth name was Benjamin Grossbaum.
- His family moved to New York City when he was a child.
- His father died young, leaving the family in poverty—an early experience that shaped Graham’s lifelong focus on financial security and prudence.
- Despite hardships, he excelled academically and won a scholarship to Columbia University, graduating at age 20 (1914) as salutatorian.
Wall Street Career (1914–1929)
- Joined Wall Street immediately after graduation, starting as a messenger and clerk at Newburger, Henderson & Loeb, then quickly rising to become a partner.
- By his mid-20s, Graham was earning over $500,000 per year (equivalent to millions today).
- He developed a reputation for deep financial analysis, spotting mispricings and arbitrage opportunities.
- In 1926, co-founded the Graham-Newman Partnership, one of the earliest hedge-fund-like investment partnerships.
The Crash and Lessons (1929–1932)
- The Great Depression nearly wiped him out financially.
- This failure humbled Graham and led him to develop safer, more disciplined approaches to investing.
- He emphasized downside protection and the idea of a “margin of safety”—buying securities well below their intrinsic value to limit risk.
Pioneering Value Investing (1934–1949)
- In 1934, with David Dodd, he published “Security Analysis”, a groundbreaking textbook that laid the foundation of value investing.
- Taught at Columbia Business School, where his lectures attracted future legends like Warren Buffett, Irving Kahn, and Walter Schloss.
- Advocated analyzing financial statements, rejecting speculation, and focusing on intrinsic value.
- Promoted net-net investing: buying stocks trading for less than the company’s net current assets.
The Intelligent Investor (1949)
- Published “The Intelligent Investor”, which simplified his principles for individual investors.
- Introduced the concept of Mr. Market (an allegory of market irrationality).
- Advocated two investor profiles:
- Defensive investor (passive, focuses on diversification and safety).
- Enterprising investor (active, seeks bargains with skill and discipline).
Warren Buffett later called this book “the best book about investing ever written.”
Later Years and Retirement (1956–1976)
- Retired in the mid-1950s, closing Graham-Newman Corp. in 1956.
- Moved to California and spent his time teaching, writing, and enjoying life.
- Distanced himself from active investing, believing markets had become more efficient.
- Passed away on September 21, 1976, in Aix-en-Provence, France, at age 82.
Legacy
- Known as the “Father of Value Investing.”
- His disciples (Buffett, Kahn, Schloss, Klarman indirectly) carried his philosophy forward.
- Concepts like margin of safety, intrinsic value, Mr. Market, defensive vs. enterprising investors remain central to modern investing.
- His teachings underpin fundamental analysis, long-term investing, and risk management worldwide.
✅ In summary: Graham went from poverty to Wall Street success, nearly lost everything in the Great Depression, then rebuilt his philosophy into a disciplined system that still guides investors today.
Benjamin Graham’s Journey Snapshot

Pingback: Top Investors - My Finance Guide – Expert Trading Strategies, Portfolio Management & Market Insights